Nutritional parameters of "mate cocido" with milk prepared from two species of Ilex and their commercial mixture for school age population
Keywords:
Chá mate, Ilex dumosa, Ilex paraguariensis, Mate cocido, Mate cocido with milk, nutritional value, schoolchildren dietAbstract
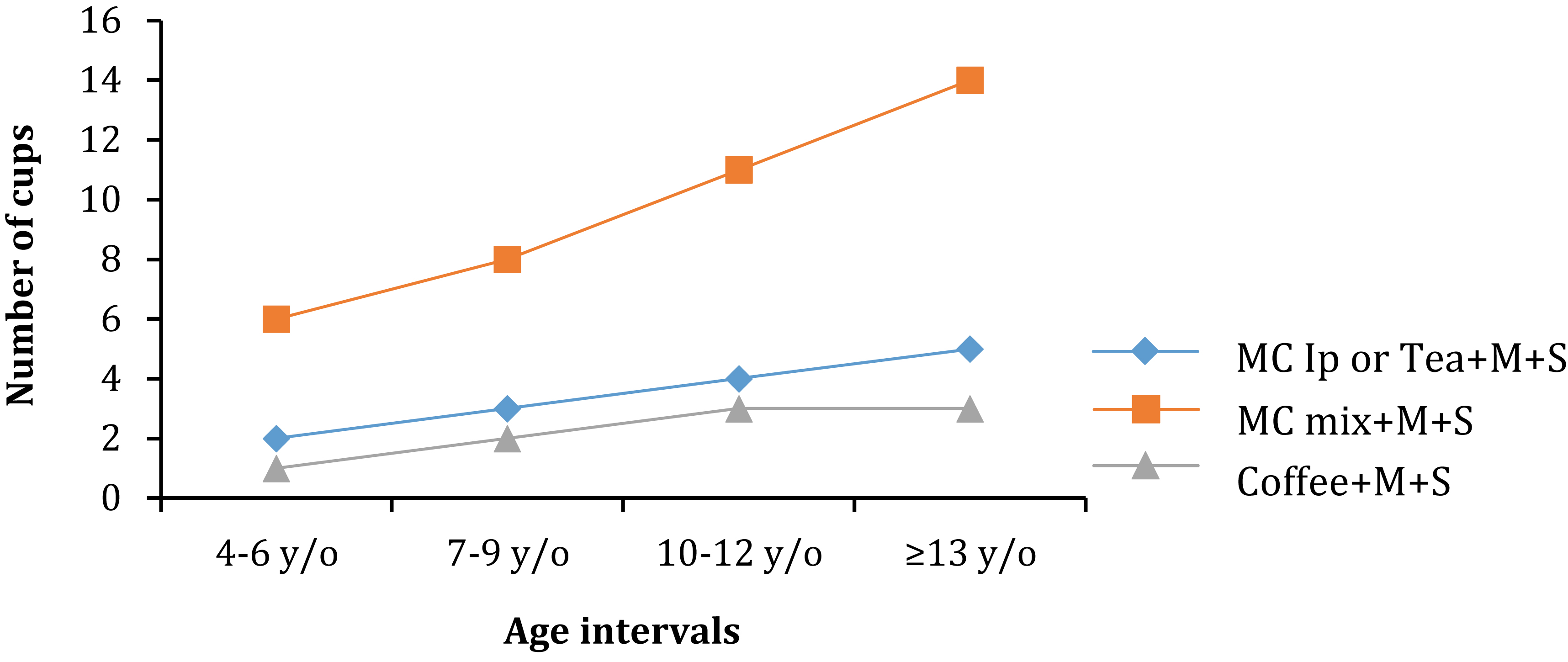
The infusion at 1.5% of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis A.St.-Hil.) (Ip) corresponds to "cooked mate" (MC), whose combination with milk (50:50 v/v) (M) and refined sugar (S) is the "mate cocido with milk", a popular food in southern South America offered to preschool and primary education students (3-13 years old) in Argentina. Another species of the genus, I. dumosa Reissek (Id), has low caffeine; appears in the market as an Id:Ip (70:30 w/w) mixture. The substitution of Ip by the mentioned mixture maintains analogous nutritional values and significantly lowers the caffeine levels (α=0.05); this allows for a higher consumption of the food during the day, without reaching the xanthine daily limits (40-100 mg day-1) for the age range, favoring the students intellectual and physical performance without adverse effects. The daily intake of a double serving (breakfast and afternoon snack) of MC+M+S provides high energy and is a source of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins A, B1, B2, B5, B6, and B12, biotin and essential minerals (Mn, P, Zn, Cu, Ca, Mg, Na, Cl, K, Fe and Al), with low cholesterol. The nutritional parameters are within international limits. Heavy metals do not make it to the infusion or they remain well below harmful values.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.


