Small farmers' perception of factors influencing regional chemical control of Diaphorina citri
Keywords:
regional control areas, Candidatus Liberibacter, chemical control, growers' perceptionAbstract
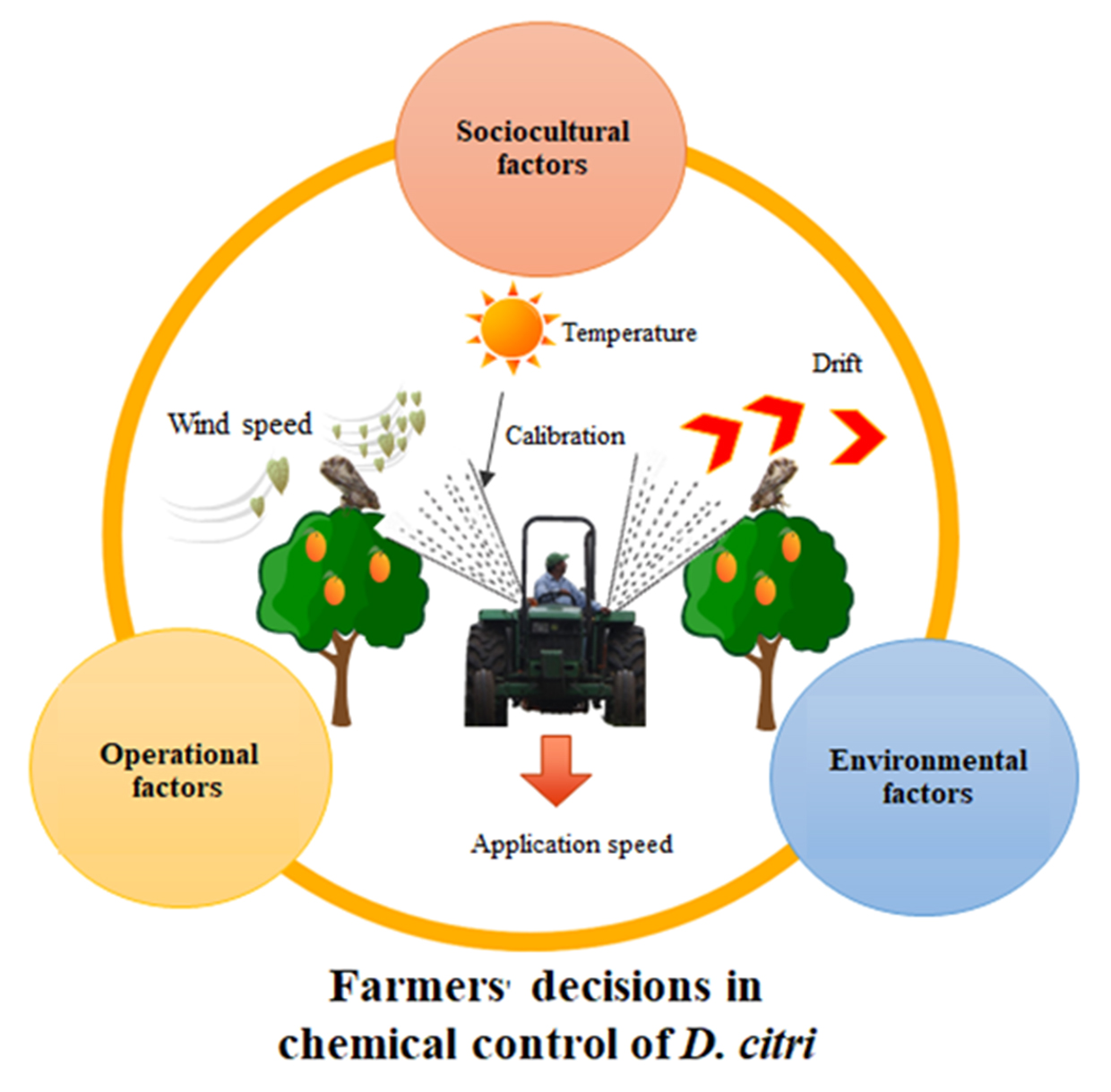
Regional Control Areas (RCAs) have been implemented in Mexico as a strategy to delay the spread of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus, the causal bacterium of the disease known as Huanglongbing (HLB). The implementation of an effective management of the vector insect, Diaphorina citri in the RCAs requires the knowledge, acceptance and coordinated engagement of small agricultural producers. This research assessed the perception and knowledge of 62 citrus growers regarding the operational, sociocultural and environmental factors influencing chemical control of D. citri in four RCAs within Veracruz State. According to their responses, the following factors have been identified as the operational factors with the highest influence on the effectiveness of insecticides against D. citri within RCAs: the lack of knowledge about the use of surfactants, application speed, poor calibration of sprayers and incorrect water quality. The most significant sociocultural factors are the general unawareness of the pest and the safe and proper application of pesticides. The most relevant environmental factors during application: temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed. Sociocultural index correlated with the perception of effectiveness. Therefore, it becomes necessary to consider differences among citrus growers in each region and setting out the most appropriate
strategies for vector and disease management.
Highlights
- Some operational practices that citrus growers are not aware of may influence their perception of chemical control.
- The sociocultural context of growers determines their decision-taking on insecticide applications.
- During the application of insecticides in regional control areas (RCAs), growers do not take into account weather conditions.
- The effective management of D. citri requires a coordinated engagement of small growers' in RCAs.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.



