Residual effect of two sewage sludges from a phytoremediation test with thistle on camelina (Camelina Sativa (l.) Crantz) in Madrid
Keywords:
Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz, Cynara cardunculus L., thermally-dried sewage sludge, composted sewage sludge with pruning wasteAbstract
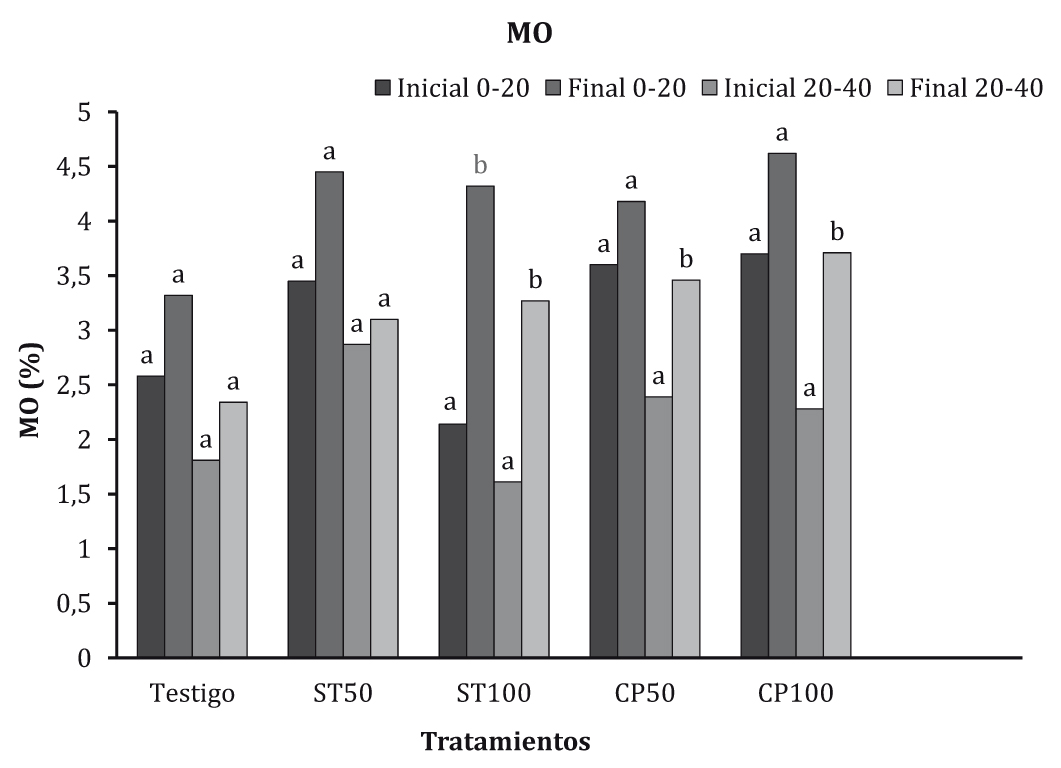
A field trial with Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz was performed to study their behavior following a residual of previous crop fertilization in a representative soil of a semiarid agroecosystem. The experimental design consisted of plots sown with Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz in crop rotation with Cynara cardunculus L. and using their residual fertilizer amendments (ST50) and (ST100) thermally-dried sewage sludge and (CP50) and (CP100) composted sewage sludge with pruning waste, which were compared with a control soil (control). Overall, fertilization thermally-dried sewage sludge (ST50) improved crop response, increasing production values compared to control and fertilization with composted sewage sludge with pruning waste. Moreover, with the residual effect of the thermally-dried sewage sludge (ST50) a more efficient utilization of the applied nitrogen (protein) is achieved, as well as a higher fat content. Regarding the physicochemical properties of soil, the results show that the soil fertilized with sludge had an increase of pH, organic matter, P, K, Ca, Mg and Na. The concentration of micronutrients Cu, Zn and Ni and heavy metals Cr, Cd and Pb increase over the control, but there was no risk of contamination.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.



