First report of Berkeleyomyces basicola (synonymous: Thielaviopsis basicola) on roots of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam) in Argentina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.027Keywords:
Ipomoea batatas, root rot, Chalara elegans, potato, sweet potato fungal diseaseAbstract
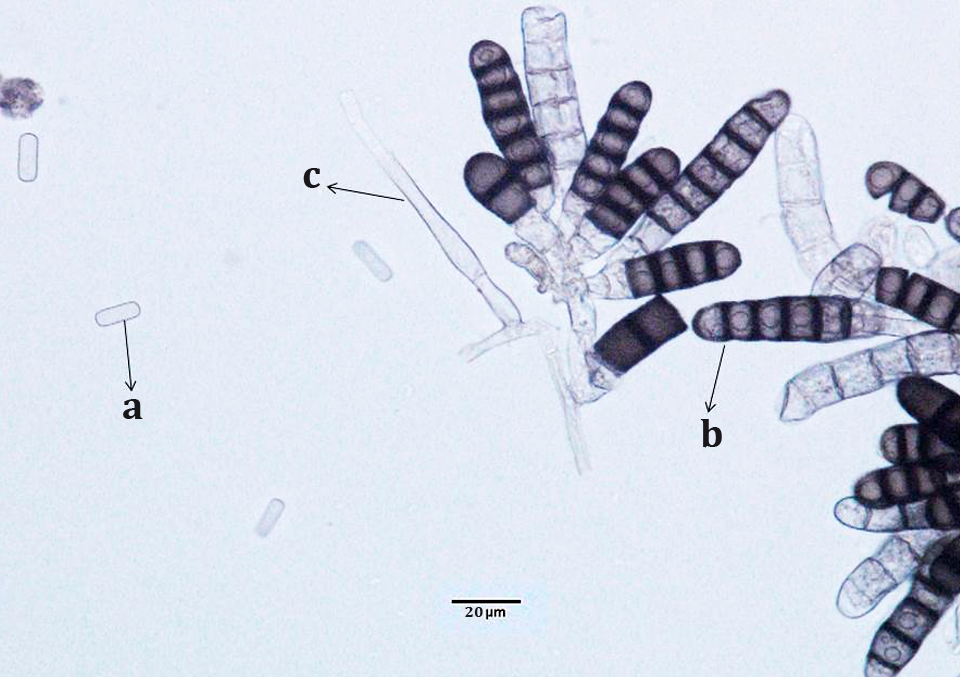
Symptomatic sweet potato cv Arapey INIA samples were collected from a commercial production field in Colonia Molina, Guaymallén department, Mendoza province, Argentina. They showed dark rounded lesions, sometimes coalescing with white granular mycelium. Fungus was obtained from symptomatic sweet potatoes, which represented the generalized infection that affected the crop. They were seeded in PDA with streptomycin sulfate and incubated for seven days at 21°C, alternating white/black (UV400nm) light. Observations with an optical microscope revealed the presence of hyaline, not septated, cylindrical endoconidia with rounded ends. They were 8-16 μm length and 4–6 μm width. Phialides were 43-46 μm length, rounded bases (7-9 μm width) and tapering to the neck´s tip (4-6 μm width). Brown chlamydospores (aleuriospores), 9-13 μm length and 8-12 μm width, in chains of 2-8 spores were observed. For molecular identification, total genomic DNA was extracted. ITS fragment of 565 pb was amplified using ITS5/ITS4 primers and sequenced. The sequence indicated 99% identity with Berkeleyomyces basicola (synonymous: Thielaviopsis basicola). This was deposited in GenBank as (KX580957) (CBS: C430.74, Gen Bank accession number AF275482.1). This is the first report of B. basicola in sweet potato in Argentina, a potential threat to storage root yields.
Highlights:
- Sweet potato black root rot, new disease in Argentina.
- First report of Berkeleyomyces basicola causing black root rot on sweet potato in Mendoza, Argentina.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.


