Modeling of the spatial distribution of Bactericera cockerelli Sulc. (Hemiptera: Triozidae), in Solanum tuberosum L. (Solanales: Solanaceae)
Keywords:
geostatistics, kriging, spatiotemporal stability, paratrioza, zebra chipAbstract
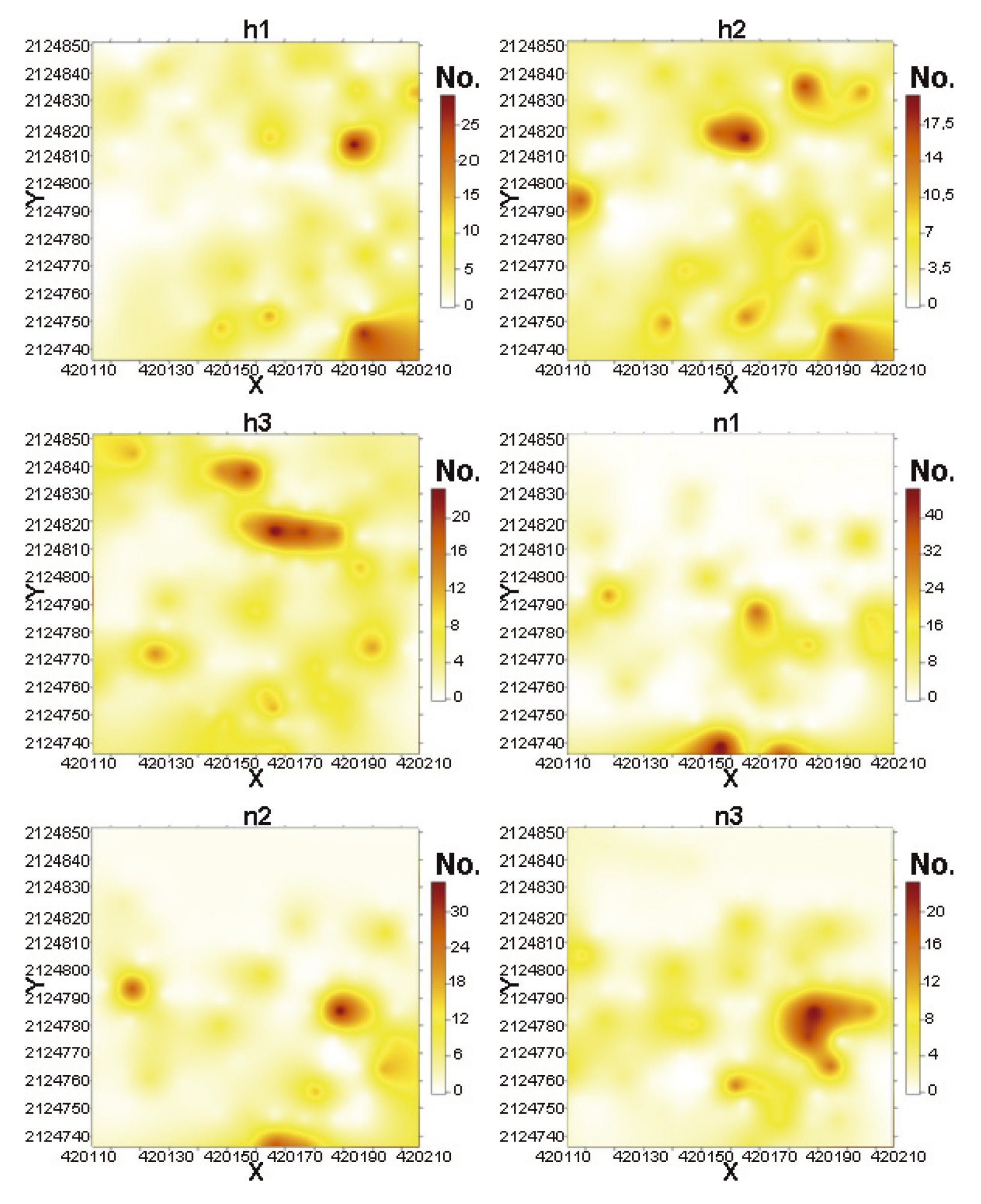
The production of Solanum tuberosum L., Lycopersicum esculentum Mill. and Physalis ixocarpa Brot. (Solanales: Solanaceae) is prone to economic loses because of the presence of Bactericera cockerelli Sulc., which is related to the Purple Top and “zebra chip” diseases, and is also considered a vector of Candidatus Liberibacter solanacearum. The alternatives of control have been inefficient because none of them have considered the spatial behavior of the insect inside the plot. Such behavior would allow focusing the control alternatives, making them more efficient. The purpose on this work was to model the spatial distribution of the eggs, nymphs and adults of B. cockerelli which were obtained in potato field by transects samplings, by using geostatistics tools. The results indicate that the spatial distribution of the populations of eggs, nymphs and adults of B. cockerelli type was aggregated in each sampling date. The cross validation of the semivariograms corroborates the aggregated distribution of eggs, nymphs and adults of B. cockerelli. The generated maps allow observing the aggregated structure of the insect population, letting identify both infested areas and not-infested areas. Spatiotemporal stability was found for the three stages of the insect.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.


