Assessment of population structure and management of Cordia dodecandra A. DC. in homegardens and tropical forest in Yucatan, Mexico
Palabras clave:
agroforestería, conservación de árboles tropicales, especies nativas multipropósito, reservorios de germoplasmaResumen
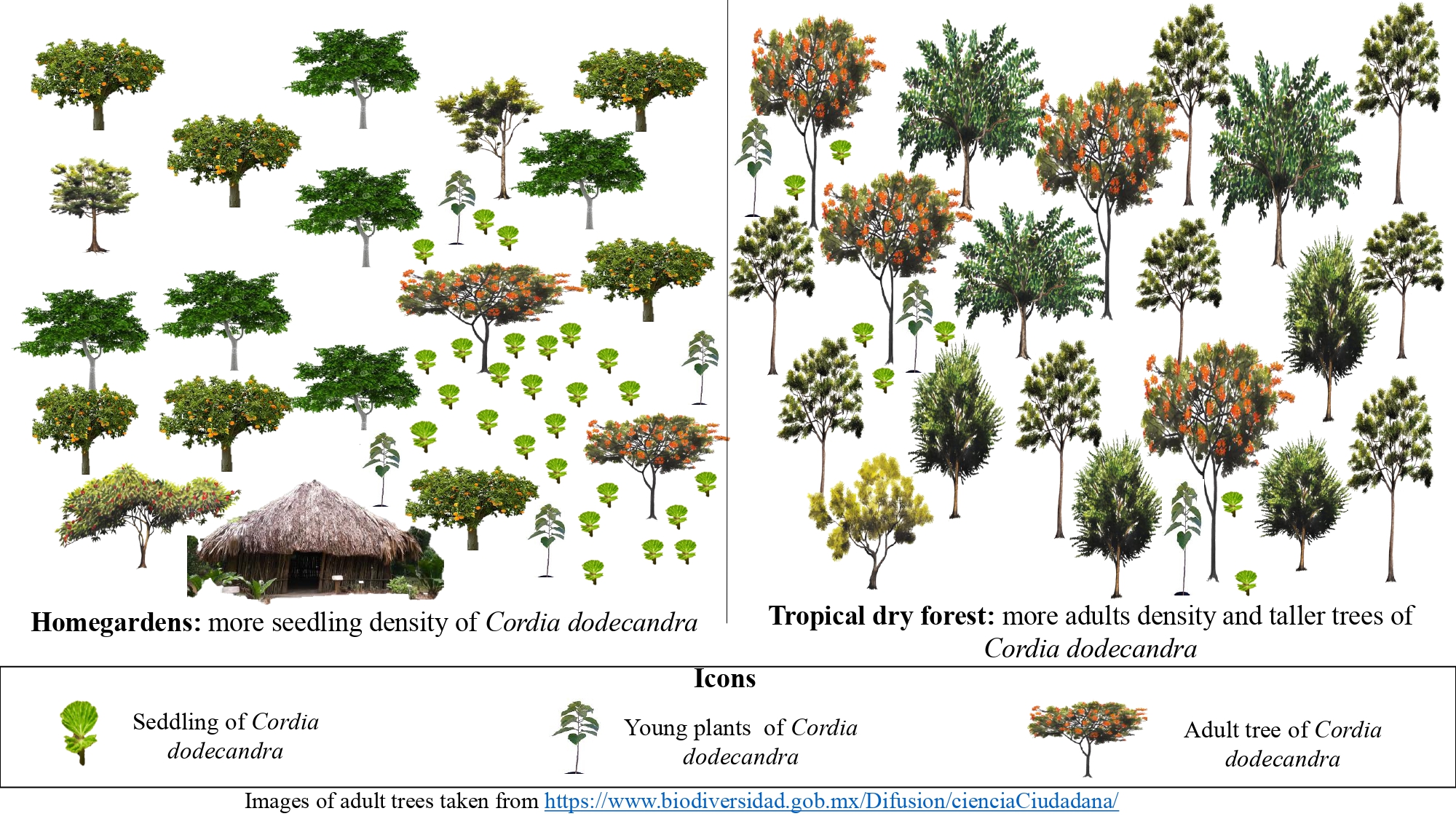
Cordia dodecandra A. DC. is an arboreal component of forests and Maya homegardens in the state of Yucatan, México. Changes in land use and landscape fragmentation have led to declines in wild populations. Understanding this species’ population structure is relevant to determining the current state of its populations and proposing strategies for its conservation. The population structure of C. dodecandra in forest and homegardens in Yucatan, and the management practices associated with the species were documented with interviews. Relative importance of the tree species in the associated vegetation was estimated. Seedling density (< 1m of height) was higher in the homegardens than the forest with an evident decrease in the density of juvenile individuals caused by practices such as weeding. In contrast, the forest contained a greater number of adult and larger individuals than in the homegardens. Individual C. dodecandra were taller in the forest, but those in the homegardens had a larger diameter at breast height. Although it has multiple uses (e.g. food, ornamental, wood) the C. dodecandra in homegardens received only minimal maintenance, possibly threatening its permanence in this system. This is concerning since the homegardens function as de facto germplasm banks for this species.
Highlights
- Cordia dodecandra trees from homegardens have a diameter at breast height (DBH) larger than those that live in the dry forest.
- Cordia dodecandra trees in tropical dry forests, are taller than in homegardens.
- Succession data showed that tropical dry forests have more adult trees of Cordia dodecandra, and homegardens have a higher density of seedlings.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.


