Opuntia ellisiana Griffiths as livestock feed in areas similar to USDA cold hardiness zones 6-7
Palabras clave:
Opuntia ellisiana, filogenia, ecofisiología, resistencia al frío, productividad, contenido de nutrientesResumen
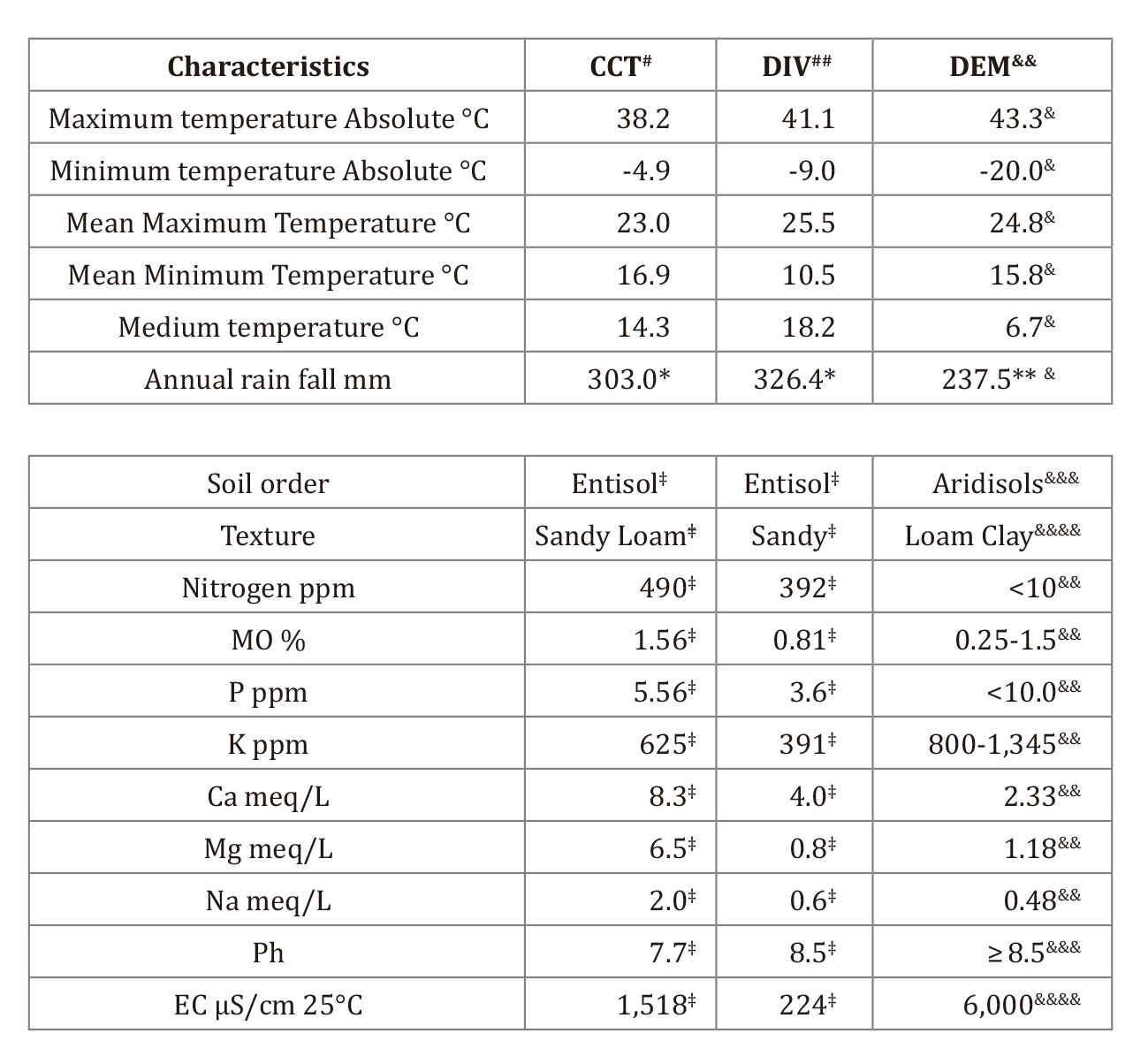
The present review compiles the studies carried out so far on Opuntia ellisiana Griffiths. This species, of unknown origin, was first described at the beginning of the 20th century in southern Texas, USA, and introduced to Argentina in 1998. This species, like other Opuntia sps., can be cultivated in a wide range of environments and its lower transpiration per unit of carbon gained in relation to C3 and C4, has lead to in an important increase in water-use efficiency. While O. ellisiana has a lower growth and productivity than O. ficus-indica (L.) Mill. it stands out for its resistance to sub-zero temperatures. Fortunately, the intraspecies variation within O. ellisiana, shortens the time for its use after establishment. There is a wide variation in the nutrient content between the different forage species and clones of Opuntia. Due to the inherently low N availability in arid ecosystems, O. ellisiana, like the other species, has low protein content in natural unfertilized conditions. Some efforts, as the use of N-fertilizer, have been carried out to improve its protein level. About 15% protein levels have been obtained with other Opuntias. Other research has been directed to provide a favorable abiotic environment for a cactus to achieve higher biomass productivity and improved protein levels by interacting with nurse plants, such as Prosopis sps. The last alternative resulted in a significant increase in protein content and cladode quantity per plant of O. ellisiana.
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




