Grain quality of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars under low and high nitrogen dose
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.012Palabras clave:
fertilización nitrogenada, genotipos, tecnología de granos, tiempo de cocción, contenido de proteínasResumen
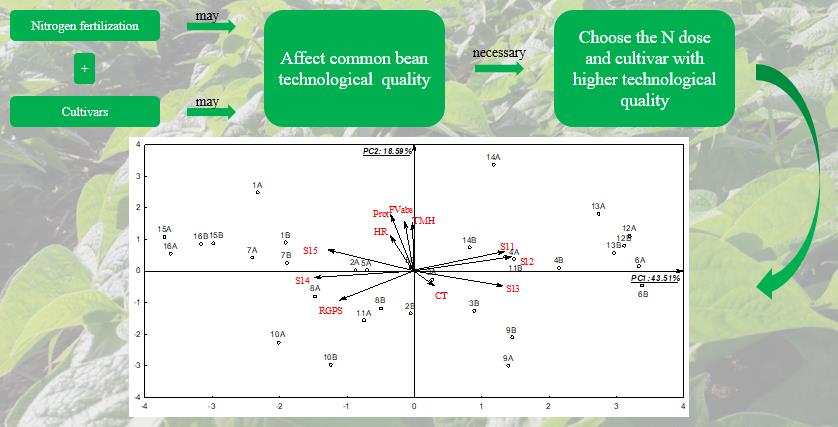
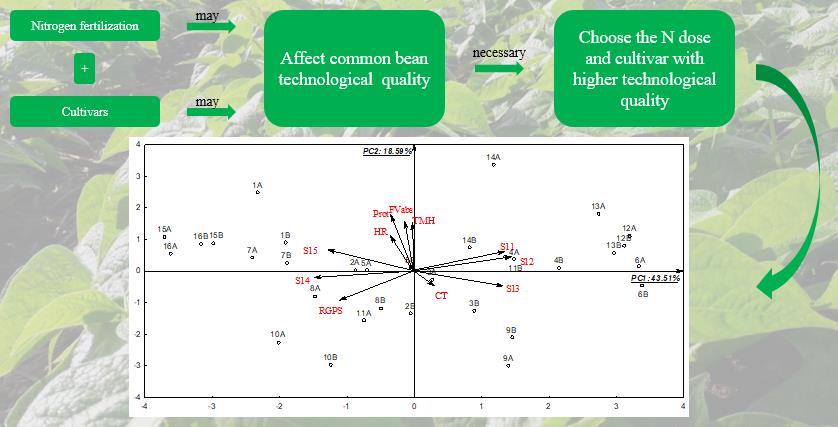
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of low and high topdressing doses of nitrogen (N) on the qualitative attributes of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars and indicate cultivars with better grain technological characteristics. The experimental design was randomized blocks in split plots, with four replicates. Plots comprised 16 common bean cultivars of the commercial grain ‘Carioca’, while subplots comprised two N doses: 20 and 120 kg ha-1 applied as topdressing. The following evaluations were carried out: sieve yield (SY), relative grain production on sieves (RGPS), crude protein content (PROT), final water volume absorbed (FVabs), time for maximum hydration (TMH), hydration ratio (HR), cooking time (CT) and resistance to cooking (RC). The results were subjected to analysis of variance by F test and means were grouped by the Scott-Knott test. Multivariate principal component analysis was used to identify processes. Grain quality of common bean resulted to be more dependent on the genotype studied than on the agricultural management, such as nitrogen fertilization. Increasing N dose applied as topdressing increased grain size and protein content, but had little influence on grain hydration. FVabs and CT depended on the interaction between cultivar and N doses. Although low value, CT had an inverse correlation with PROT. The cultivars BRSMG Uai, IAC Alvorada, TAA Dama and TAA Bola Cheia showed the best grain quality characteristics.
Highlights:
- Cultivar interferes more in the common bean technological quality than nitrogen fertilization.
- Grains crude protein content had an inverse correlation with the cooking time.
- Nitrogen fertilization increases the grains size and crude protein content of common bean, but with little influence in grain hydration.
- The cultivars BRSMG Uai, IAC Alvorada, TAA Dama and TAA Bola Cheia have the best grain quality characteristics.
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2018 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 3.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




