Advances in the etiology of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam) yellow curling disease in Argentina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.087Palabras clave:
Ipomoea batatas, sweet feathery mottle virus, sweet potato virus G, sweet potato leaf curl virus, sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus, Arapey INIA, postulados de KochResumen
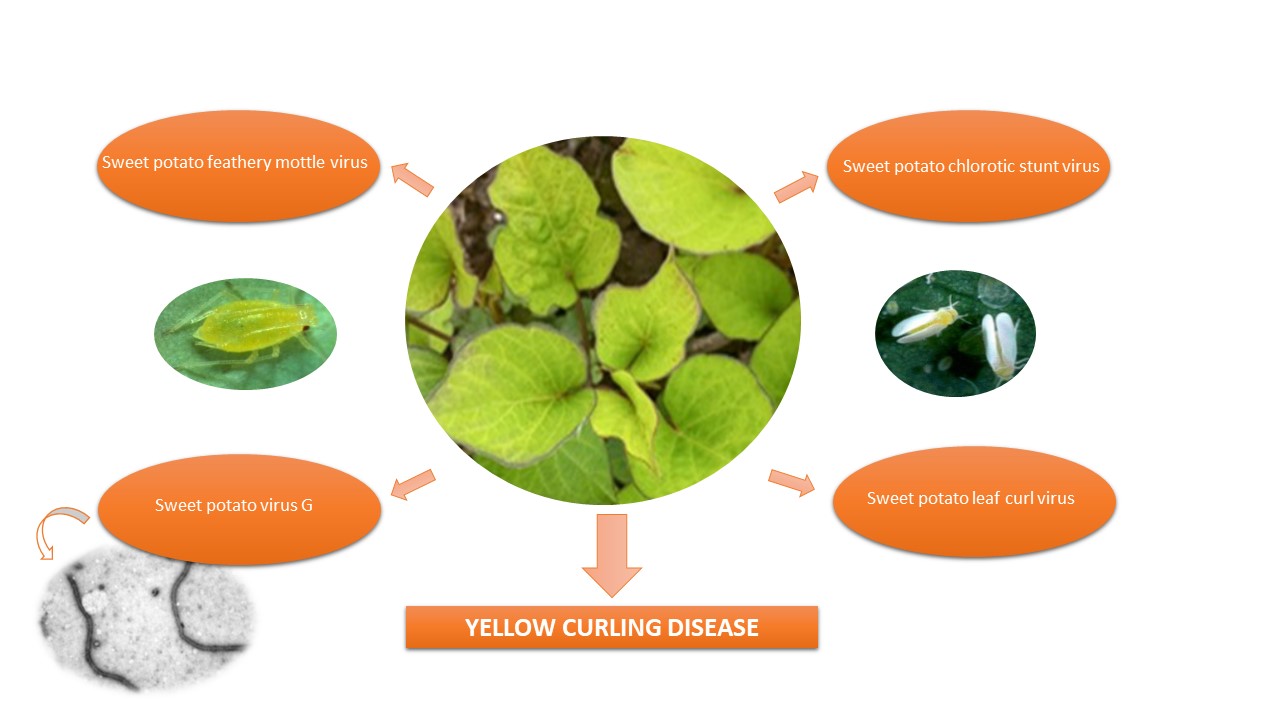
Sweet potato yellow curling (YC), the most severe disease of sweet potato detected in Argentina, causes symptoms and damage to sweet potato crops in all cultivated regions. Since 2010/11, the presence of four viruses has been detected in symptomatic cv. Arapey INIA: two potyviruses non-persistently transmitted by Myzus persicae (sweet potato feathery mottle virus, SPFMV and sweet potato virus G, SPVG); a closterovirus, sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus (SPCSV) and a geminivirus, sweet potato leaf curl virus (SPLCV), both transmitted by Bemisia tabaci in a semi-persistent and persistent manner, respectively. All the plants were collected from fields in Colonia Caroya, Córdoba province, Argentina. The objectives of the present work are to isolate and identify the virus or viruses involved in YC disease of sweet potato, and to elucidate the viral combination that reproduces YC symptoms. The most severe YC symptoms for this genotype in the field were only reproduced by a combination of the four viruses. The symptoms include chlorosis, stunting, mosaic, blistering, leaf curling, chlorotic spots, chlorotic patterns, leaf area reduction and distortion, and upward curling of leaf edges. The presence of each virus was detected by serological (DAS, NCM and TAS-ELISA) and molecular (PCR) tests. It is concluded that the interaction of SPFMV, SPVG, SPCSV and SPLCV is needed for the development of YC symptoms.
Highlights
- Four viruses involved in yellow curling disease, SPFMV, SPVG, SPCSV and SPLCV were isolated and identified.
- The first antiserum produced in Argentina allows the fast, safe and efficient diagnosis of SPVG.
- The interaction of SPFMV, SPVG, SPCSV and SPLCV is needed for the manifestation of yellow curling in Argentina.
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2018 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 3.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




