Influence of urban trees on noise levels in a central Chilean city
Keywords:
urban trees, noise mitigation, urban pollution, ecosystem service, noise pollutionAbstract
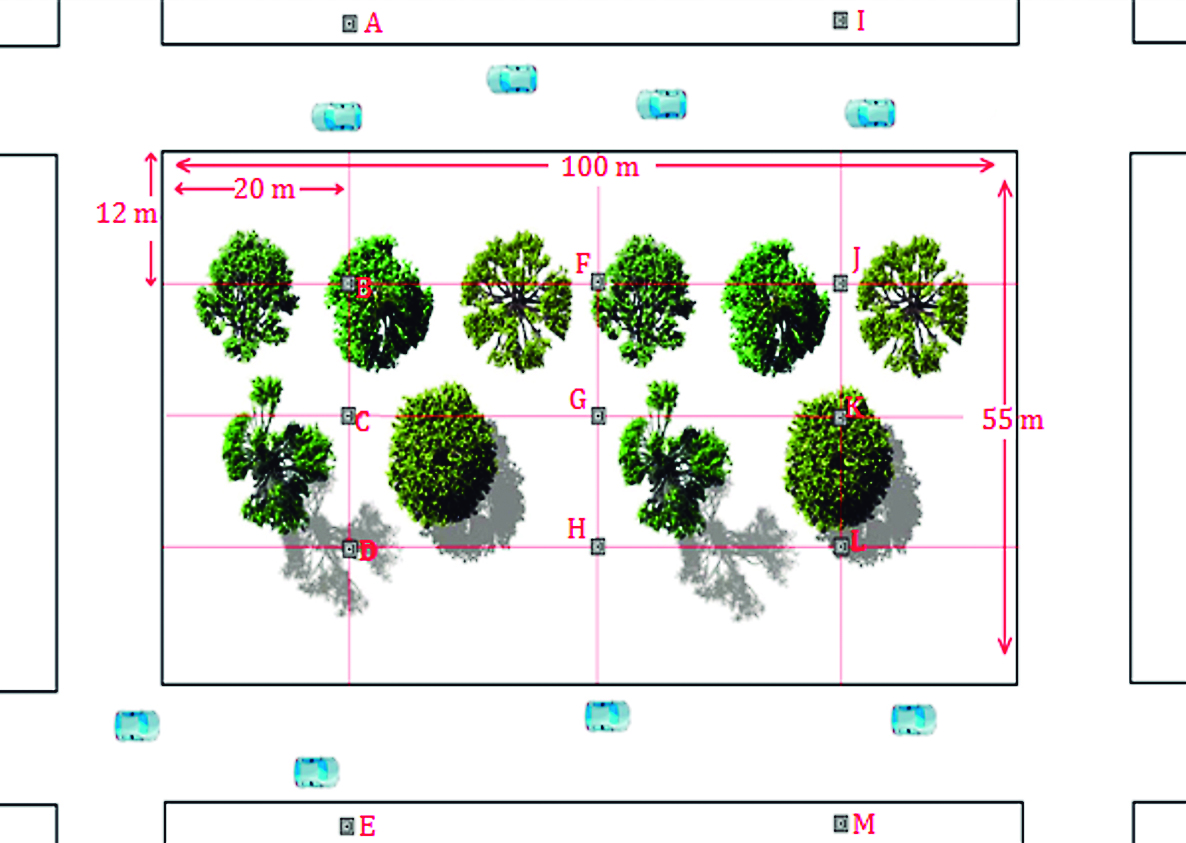
The effect of urban trees as a noise mitigating element was determined on Alameda Avenue in the city of Talca, Chile, a Mediterranean continental area. Maximum and minimum noise, especially generated from vehicles, was recorded at 13 points in four sections of the avenue for twelve days, three times a day at different distances from the edge of the street way, which generated a total of 2,080 noise records. At each point a circular plot of 201 m2 was established to determine tree and shrub coverage. The results showed significant differences of noise between the classes of coverage; however there was no relationship significant between the noise level and the increase in coverage, which can be explained by the large amplitude in the noise registers. The vegetation located at 6.5 meters from the sound source shows lower levels of noise when the coverage is increased, proving the environmental function of the vegetation in the mitigation of this pollutant agent. Regarding theses of the findings, it is necessary to implement public policies that consider urban planning, incorporating in its design greater and better availability of tree species and that certain public space are located away from sources of noise pollution.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




