Heavy metals in atmospheric dust deposited in leaves of Acacia farnesiana (Fabaceae) and Prosopis laevigata (Fabaceae)
Keywords:
pollution, arborean plants, land uses, environmental impactAbstract
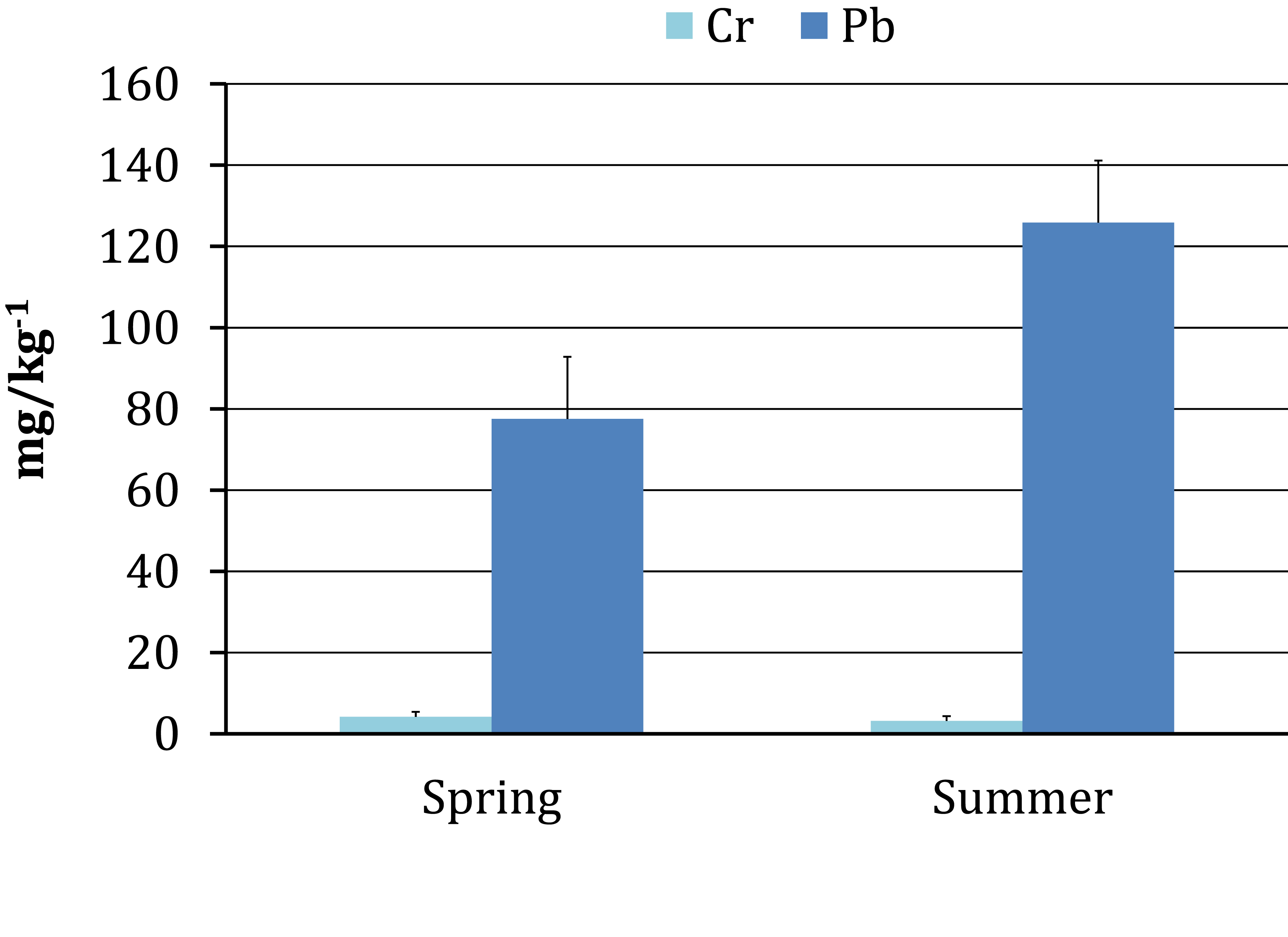
Atmospheric dust establishes an element of study to know the distribution of pollutant particles such as heavy metals and their effects on ecological systems. The objective was to determine the elemental composition of particles deposited in two species of trees as an indicator of environmental impact in San Luis Potosí, México. The distribution of Acacia farnesiana and Prosopis laevigata trees was taken into account in five soil uses to collect leaf material and extract atmospheric dust during the spring and summer seasons, determining the concentration of heavy metals using the ICP-MS technique. The results indicated the presence of Al> Cu> Zn> Pb> V> As> Ni> Cd> Ti> Cr> Co. Correlations with values of r2> 0.90 were presented between V-Ti, Ni-V, Ni-Ti, Al-Ti and Cr-V. The species factor conditioned the concentrations of Al, Ti, V, Cr, Ni and Zn mainly in the particles deposited in Prosopis leaves. Particles of nine elements were conditioned by the activities of the five land uses, where the use of mineral soil affected by the presence of Al, Cd, Co, Pb, Cu and Zn. Concentrations of Cd were 6.2 times higher in the use of mining soil than in the agricultural sector; 5.9 and 5.4 times the concentrations of Co and Pb in the use of mining soil with respect to the trade and service respectively. The season had only significant effects on Cr and Pb particles. This study indicates the existence of pollutants that can affect ecological systems so it falls within the context of continued evaluation of environmental impacts.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.



