Perception of residents on the development of the micer region Tierra of Palmares from the integrated rural tourism perspective
Keywords:
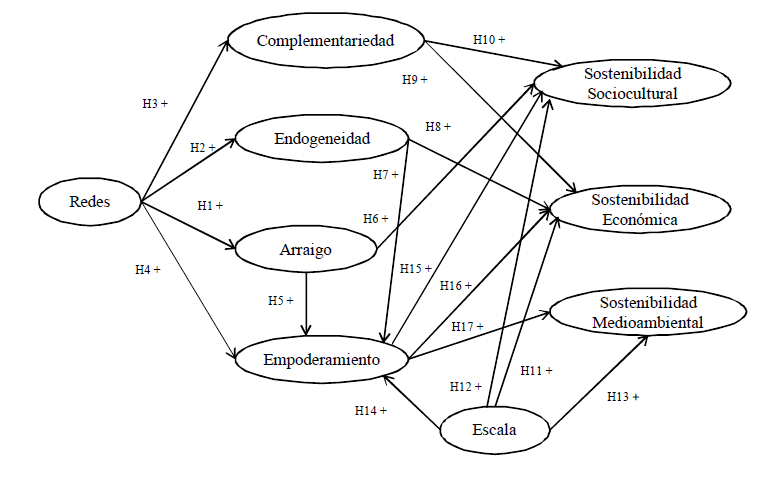
integrated rural tourism, residents "micro-region, networks, embeddedness, endogeneity, complementarity, empowerment, economic sustainability, sociocultural sustainability, environmental sustainabilityAbstract
The objective of this work is to analyze the perceptions of residents regarding the variables involved in developing Integrated Rural Tourism (IRT), as well as analyze how those variables affect said development. Therefore, we have analyzed the specific case of the residents of Tierra de Palmares, which is an area involved in a tourism development project. The residents constitute one of the main actors involved in the successful development of this type of tourism. The descriptive analysis performed as well as the Principal Components analysis shows the residents perceive the existence of key variables for reaching the desired type of tourism. Thus, it is verified that there is cooperation between the agents involved and the embedded, endogenous and complementary nature of the tourism activities that are developed, which activities allow empowering the residents. Moreover, it seems that positive effects are being generated by tourism, given that the existence of economic, sociocultural and environmental sustainability is perceived. The results of the regressions performed show that the effects of all these variables on the development of IRT are positive, although they should be analysed more in depth. Thus, the positive effect on IRT of the existence of information networks, the empowerment of residents, the development of tourism as complementary to traditional activities and the sharing of resources with tourists is detected. However, the inclusion of sustainability in the regression dilutes the effect exerted by complementarity and sharing. These results demonstrate the need to establish indirect relationships between all potentially determinant variables of TRI, which would improve the understanding of their development.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




