Identification of agronomic interesting QTL in the segregating generations of a tomato second cycle hybrid
Keywords:
Solanum section Lycopersicon, plant breeding, plant genetic resources, fruit quality, post-harvest life, plant biotechnology, quantitative trait loci (QTL)Abstract
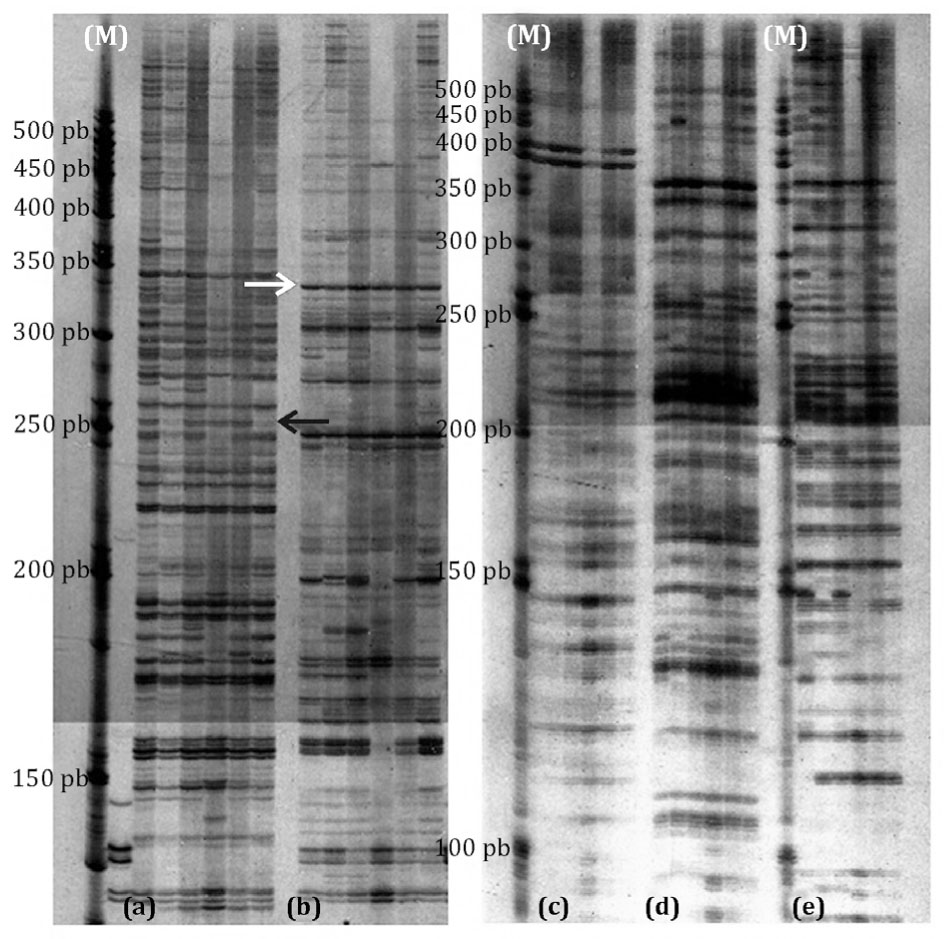
The objective was to detect QTL of agronomic interest in the segregating generations F2 and backcrosses of a tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) second cycle hybrid (SCH) obtained between two recombinant inbred lines derived from the interspecific cross S. lycopersicum cv. Caimanta x S. pimpinellifolium LA 722. Molecular characterization was achieved by AFLP markers and agronomic traits under study were fruit weight, diameter, height, soluble solids content, acidity, color, pH, shape, firmness and postharvest life. Single point analysis was applied to detect QTL, assessing the association of AFLP polymorphic bands and quantitative traits with significant genetic variance. Amplifications with six primers combinations, selected because of detecting high polymorphism percentage, 221 AFLP bands were obtained, and 135 (61.1%) of them were polymorphic in the tomato populations analyzed. In the F2 population, 29 polymorphic fragments adjusted to the expected mendelian segregation and a total of 28 QTL were detected for all evaluated traits. In the backcross population, 15 polymorphic fragments adjusted to the expected mendelian proportion 1:1 (12 of these fragments showed a de novo pattern) and a total of 13 QTL were identified for the traits soluble solids content, height, weight and diameter. AFLP allowed to identify QTL of agronomic interest in the segregating generations of a tomato SCH.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




