Characterization of potato parents based on combining ability and heterosis for searching resistance to Phytophthora infestans
Keywords:
Phytophtora infestans resistance, AUDPC, heterobeltiosis, specific heterosisAbstract
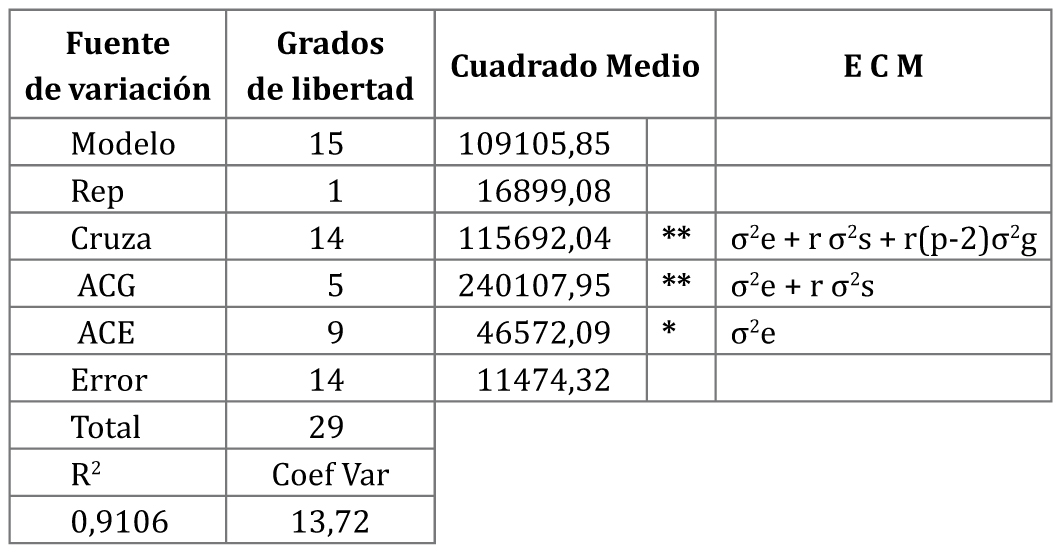
The efficient control of Phytopthora infestans results from the selection of genotypes with the capacity of transferring resistance. In order to characterize potato parents based on combining ability and heterosis for their resistance to P. infestans, six parents were crossed (Libertas, Jaspe, Chotañawi, Pollerita, Robusta and INRA 92T.114.76). The 15 tuber families of second clonal generation obtained were inoculated with P. infestans in Balcarce (Buenos Aires, Argentina) and evaluated under randomized complete block design with two replicates. Area Under Disease Progress Curve (AUDPC) was recorded for each genotype; general and specific combining ability, average heterosis, heterobeltiosis, specific heterosis and broad-sense (H2) and narrow (h2) heritability were estimated. Combining ability was significant. The Robusta parent reduced the disease estimated by AUDPC; Robusta x Chotañawi was the best hybrid, as observed by the high negative value of specific combining ability. One third of the crosses expressed significant additive effects for all levels of heterosis. Hs values showed equivalence with the percent reduction of AUDPC. The obtained heritabilities (H2=0.63 and h2=0.54) indicated that selection based on the low AUDPC values can be effective. Robusta parent and Robusta x Chotañawi cross are good genotypes for transmitting resistance to P. infestans.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.










.jpg)




