Effect of foliar copper application on yield and anthocyanin concentration in Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces
Keywords:
Hibiscus sabdariffa, anthocyanins, ascorbic acid, titratable acidityAbstract
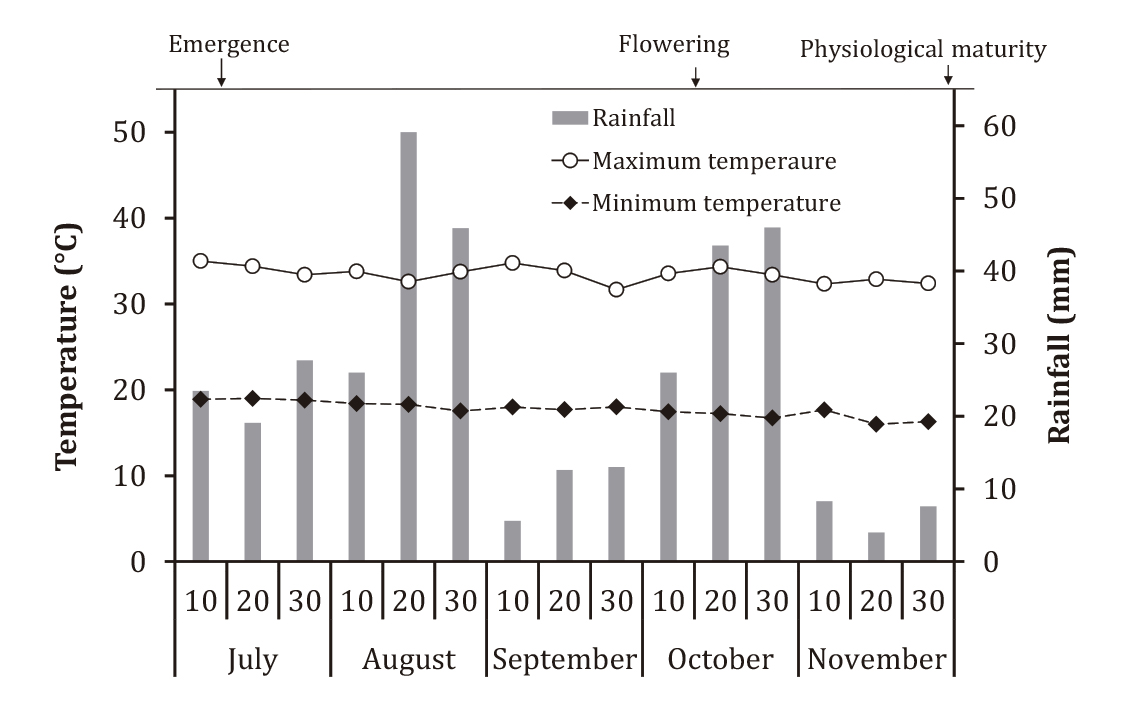
Frequent anthocyanin consumption improves health and prevents diseases due to its antioxidant activity. Exposure of some plants to high concentrations of heavy metals may increase anthocyanin concentration and thus improve their food quality. This study determined the effect of Cu spraying on hibiscus (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) leaves at various dosages and number of doses on anthocyanin content, physical and chemical characteristics, and calyces yield. For this purpose, hibiscus genotype Reina Roja was grown under rainfed conditions. During the vegetative stage, Cu was sprayed two, four or six times with 150, 300 and 450 mg L-1. The results indicate that four and six sprayings with 150, 300 and 450 mg Cu L-1 reduced dry calyces yield. Two sprayings at either Cu dosage did not modify calyces yield. Added Cu increased significantly anthocyanin content and titratable acidity and decreased ascorbic acid content in the calyces. Anthocyanin content increased the most (57 and 44%) when Cu was sprayed six times at 300 and 450 mg L-1. The data suggests that two sprayings with 150 mg Cu L-1 could improve nutritional quality of hibiscus extracts without affecting dry calyces yield.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




