Production and physicochemical characterization of genotypes of Eugenia uniflora L.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.077Keywords:
climatic conditions, Eugenia uniflora L, exotic fruits, genetic variabilityAbstract
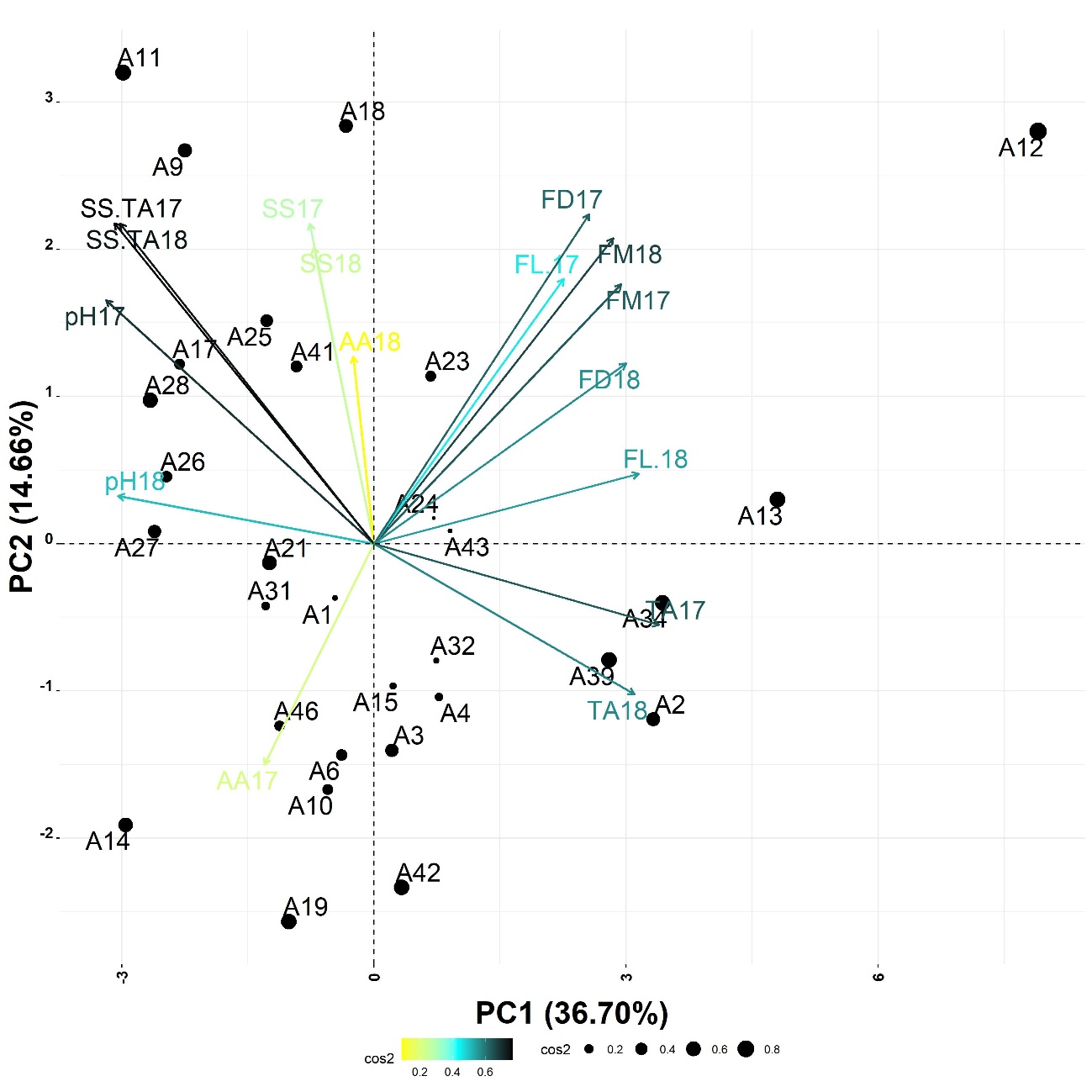
Pitanga (Eugenia uniflora L.) is an exotic fruit species of significant economic importance. However, due to genetic variability, its exploitation is hampered by the lack of homogeneous fruit production. In this scenario, this study aimed to select pitanga genotypes according to the physical and physicochemical parameters of fruits grown under semi-arid conditions. The study was developed at the Federal Rural University of the Semi-Arid Region with genotypes resulting from the open pollination of the pitanga variety ‘Tropicana”. Thirty-nine pitanga genotypes were evaluated for fruit mass, fruit length, fruit diameter, soluble solids (SS), titratable acidity (TA), ascorbic acid (AA), pH, and SS/TA ratio. The pitanga genotypes showed high variability. The clustering method separated the genotypes according to desirable traits. Genotype A12 showed the largest fruit sizes, whereas genotype A8 showed the highest SS and TA contents. Genotypes A2, A13, A34, and A39 showed fruits with the highest AT values. On the other hand, genotypes A11, A16, A45, A9, A26, and A44 showed the most significant contents of pH and SS/TA.
Highlights
- The grouping of two genotypes depends on the environmental conditions, mainly on the effect of two genotypes per year.
- The analysis of principal components allows selecting the genotypes based on their desired characteristics.
- The physical and chemical composition of two pitanga fruits are affected by climatic conditions, genotypes and years of cultivation.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




