Nutraceutical effects of organic Selenium and vitamin E supplementation on performance, antioxidant protection and egg quality of Japanese quails (Coturnix japonica)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.073Abstract
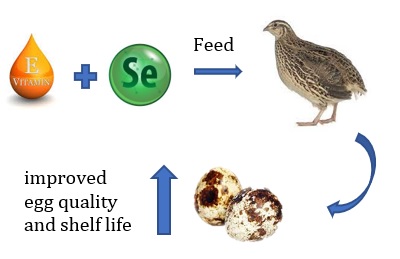
This study evaluated the nutraceutical effects of organic Selenium and vitamin E supplementation on performance, egg quality and antioxidant protection of Japanese quails. Forty-two posture cages with six birds each were randomly set in seven treatments. Each treatment consisted of the addition of 200 IU of vitamin E/kg of feed and increasing levels of organic Selenium. Significant differences were found in α-Tocopherol deposition, enzymatic activity of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and oxidative bioindicator malondialdehyde (MDA) in egg yolk with vitamin E supplementation. We concluded that supplementing 200mg of vitamin E and 0.30 ppm organic Selenium did not affect bird performance, but improved egg quality and shelf life.
Highlights:
- This study evaluated the nutraceutical effects of organic selenium and vitamin E supplementation on egg quality of Japanese quails.
- Forty-two posture cages with six birds each were randomly set in seven treatments. Each treatment consisted of the addition of 200 IU of vitamin E/kg of feed and increasing levels of organic selenium.
- Supplementing 200mg of vitamin E and 0.30 ppm organic selenium did not affect bird performance, but improved egg quality and shelf life.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




