Diet selection by the lesser rhea (Rhea pennata pennata) in Payunia, Northern Patagonia (Mendoza, Argentina)
Keywords:
arid environments, diet composition, food availability, feeding ecology, ratites, RheidaeAbstract
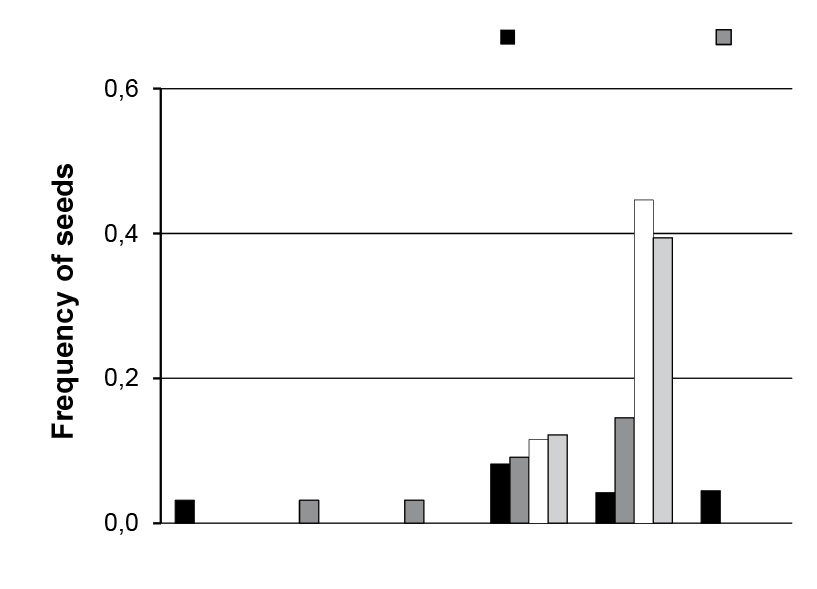
The lesser rhea (family Rheidae) is a flightless large bird of South America, threatened due to habitat loss, hunting and egg collecting, with special concern in Northern Patagonia. Diet and food availability were estimated throughout the year by micro-histological analysis and point-quadrat transects in a landscape inside and another outside the Payunia Reserve, the northernmost part of the Rhea pennata pennata distribution. Significant differences were detected by Kruskall-Wallis ANOVA, food selection by Chi-square test and Bailey’s confidence interval. A strong food selection characterized the diet of lesser rheas, dominated by leaves of shrubs and forbs, complemented by dicot seeds and a few insects. This agrees with the documented low dietary overlap with other herbivores in Payunia. Dietary changes agree with the expected from the selective quality hypothesis. Food availability was better inside than outside the protected area, with probable conservation effects for lesser rheas. Seeds, forbs and soft grasses could be for lesser rheas some key food resources to survive during unfavorable seasons in arid environments without "mallines", as Payunia. Shrubby patches, with high availability of preferred food items (tall shrubs and forbs), stood out as key habitats. Therefore, avoiding fire and woody plant removal is crucial for the conservation of lesser rheas in the northern of its range.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.










.jpg)




