Conidial germination of Botryosphaeria dothidea Mough.: Fr (Ces. & De Not.) and histological alterations on stems of pitahaya (Hylocereus undatus H.) (Haworth) Britton & Rose
Keywords:
Hylocereus undatus, dragon fruit, histopathology, stem spotAbstract
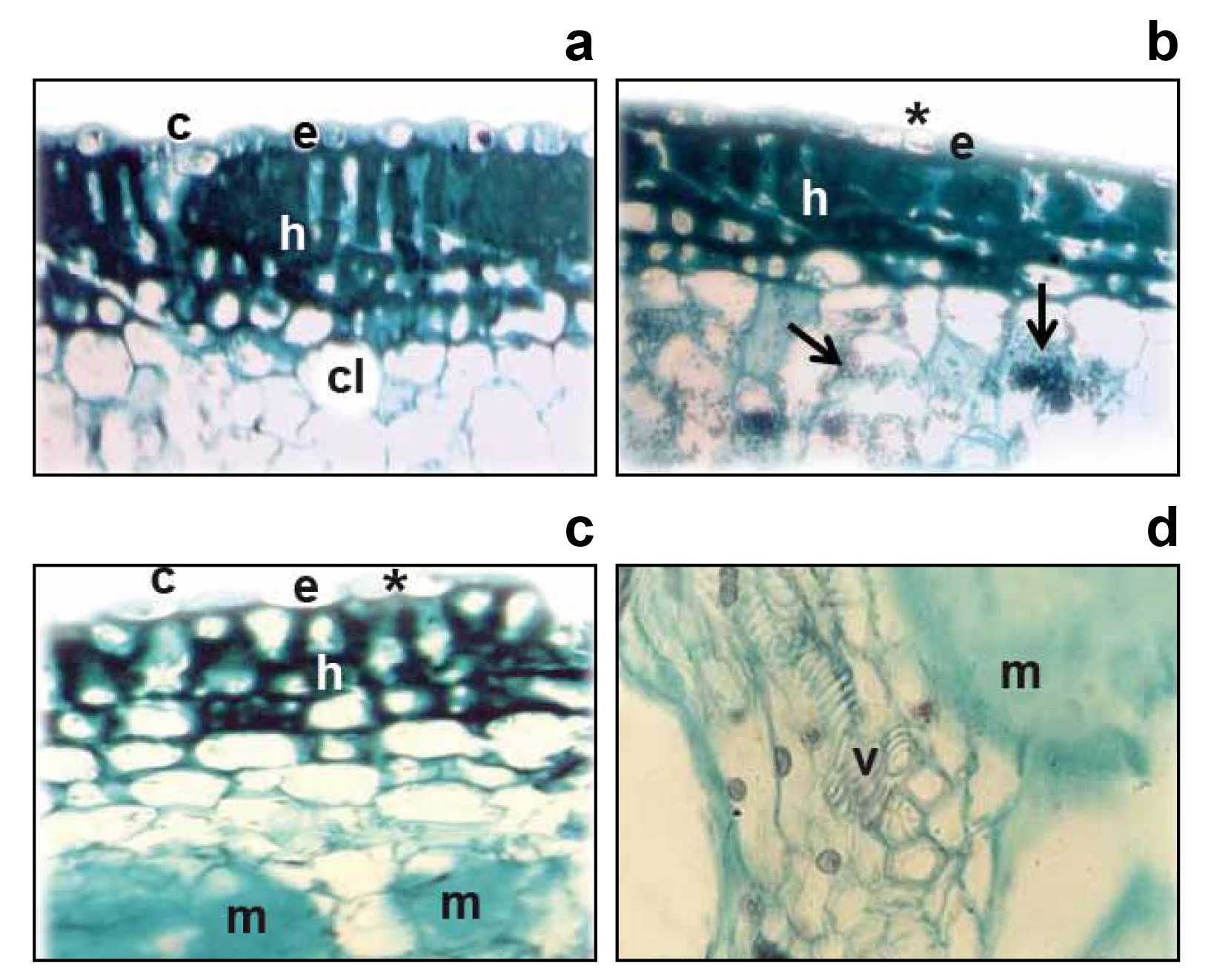
Conidial germination of Botryosphaeria dothidea (anamorph: Fusicoccum) in sterile distilled water and 1% sterile dextrose solution
was evaluated at 4, 6, 12, 24 and 36 h after incubation. Also, it was described the anatomical changes on pitahaya stems induced by this fungus, collected in the field and artificially inoculated in the laboratory. Conidial germination was less than 30% in water and it was improved when 1% dextrose was added to the water. In 1% dextrose solution the germination was 90% after 4h of incubation and 100% at 6 h. Pathogen germ tubes had entered through wounds and sometimes through stomata and hyphae colonized intra and intercellularly in the parenchyma-chlorenchyma tissues. On naturally and artificially diseased stems the main alterations were: destruction of cuticle, hyperplasia of epidermal and collenchymatous hypodermal cells and conform the advance of the pathogen a layer of lignified periderm was formed surrounding the damaged tissues; however, it couldn't stop the advance of the pathogen and the cells that surrounded the lesion suffered necrosis.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




