Effect of three different fixed-time AI protocols on follicular dynamics and pregnancy rates in suckled, dual-purpose cows in the Ecuadorian Amazon
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.130Palabras clave:
proestro prolongado, estradiol/progesterona, dispositivo de P4, IATF, preñez por IA, vacas doble propósito en lactancia, tropicalResumen
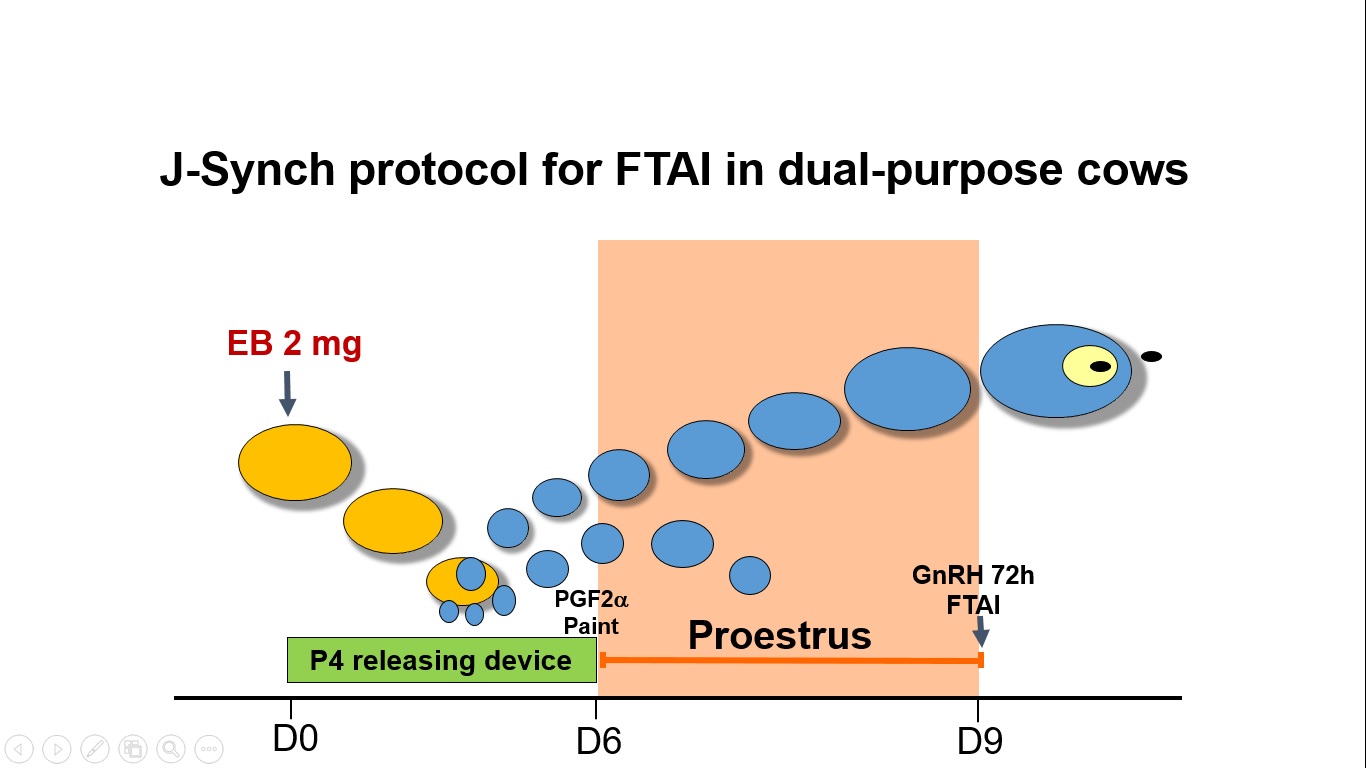
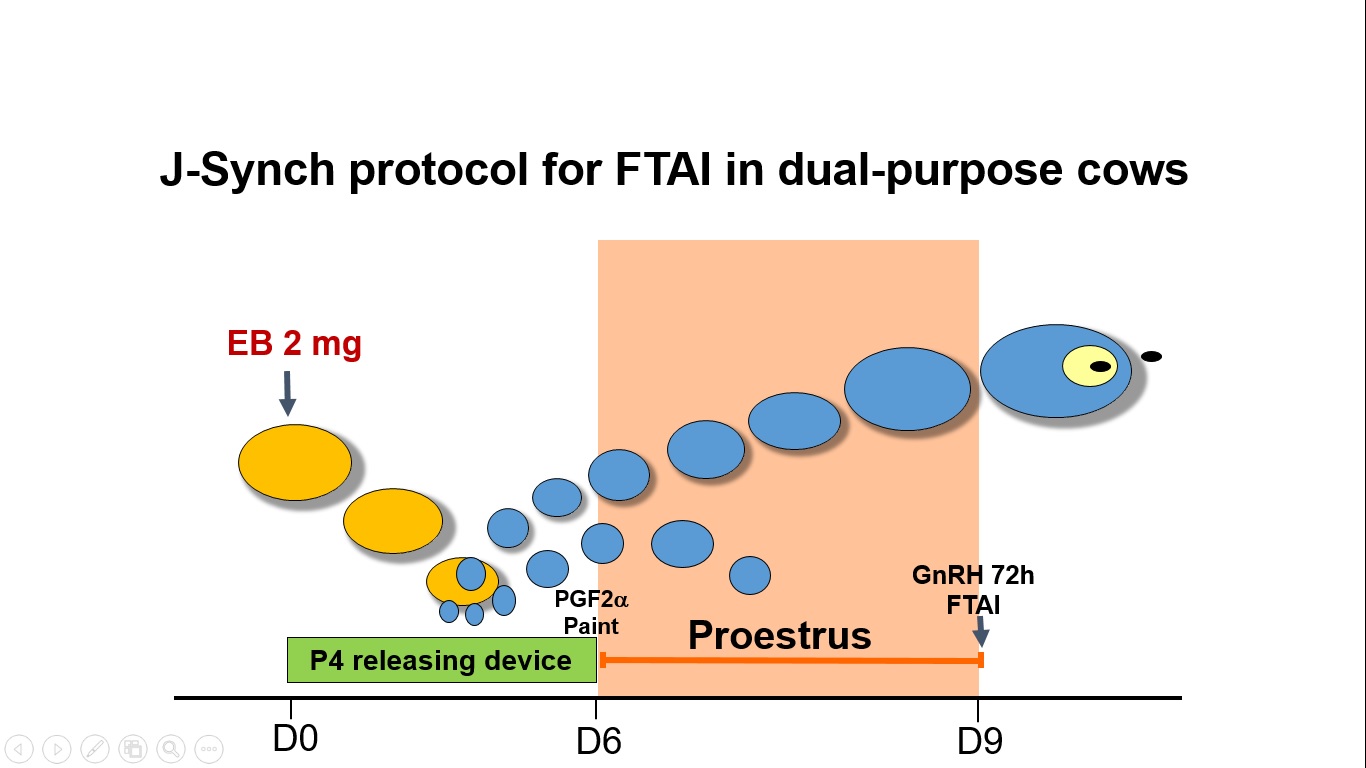
Reproductive performance is crucial for profitability of dual-purpose cow-calf production in the Ecuadorian Amazon. To evaluate three different fixed-time artificial insemination (FTAI) protocols in suckled, dual-purpose cows in the Ecuadorian Amazon. Lactating, Brown Swiss cows (n=301) received 2 mg estradiol benzoate (EB) and an intravaginal device containing 0.5 g of progesterone (P4) on Day 0. They were allocated randomly into the following three treatment groups: Cows in the EB group received 500 μg cloprostenol (PGF2α), and P4 devices were removed on Day 7, and 1 mg EB was administered on Day 8. Cows in the ECP group were treated as those in the EB group, except that they received 0.5 mg estradiol cypionate (ECP) at the time of P4 device removal on Day 7 instead of EB on Day 8. Cows in the J-Synch group had the P4 device removed and PGF2α administered on Day 6. All cows were FTAI on Day 9; cows in the J-Synch group also received 100 μg gonadorelin at that time. Although the diameter of the dominant follicle and the resulting CL were greater (P<0.05) in cows in the J-Synch group, pregnancies per AI did not differ (P>0.2) among groups (EB: 51.0%, ECP: 53.0% and J-Synch: 59.4%). The three protocols tested were applied successfully in suckled, dual-purpose cows with no differences in pregnancies per AI.
Highlights:
- Estradiol and progesterone based FTAI protocols can be successfully applied in dual purpose cows in the tropics, with P/AI ≥50%.
- Proestrus prolongation increased dominant follicle diameter at the time of FTAI and also CL diameter 7 days pos treatment
- Although differences were not significant, the protocol with the prolonged proestrus (J-Synch) resulted in higher P/AI than the two protocols with short proestrus.
- Regardless of the protocol used, there was a positive association between estrus manifestation, follicle diameter at the time of FTAI and CL diameter 7 days post treatment.
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 3.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




