A dynamic model for sodium intoxication unravels salt tolerance in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) rootstocks
Keywords:
salinity, ion exclusion, compartmentation, innate vigor, Vitis vinifera L.Abstract
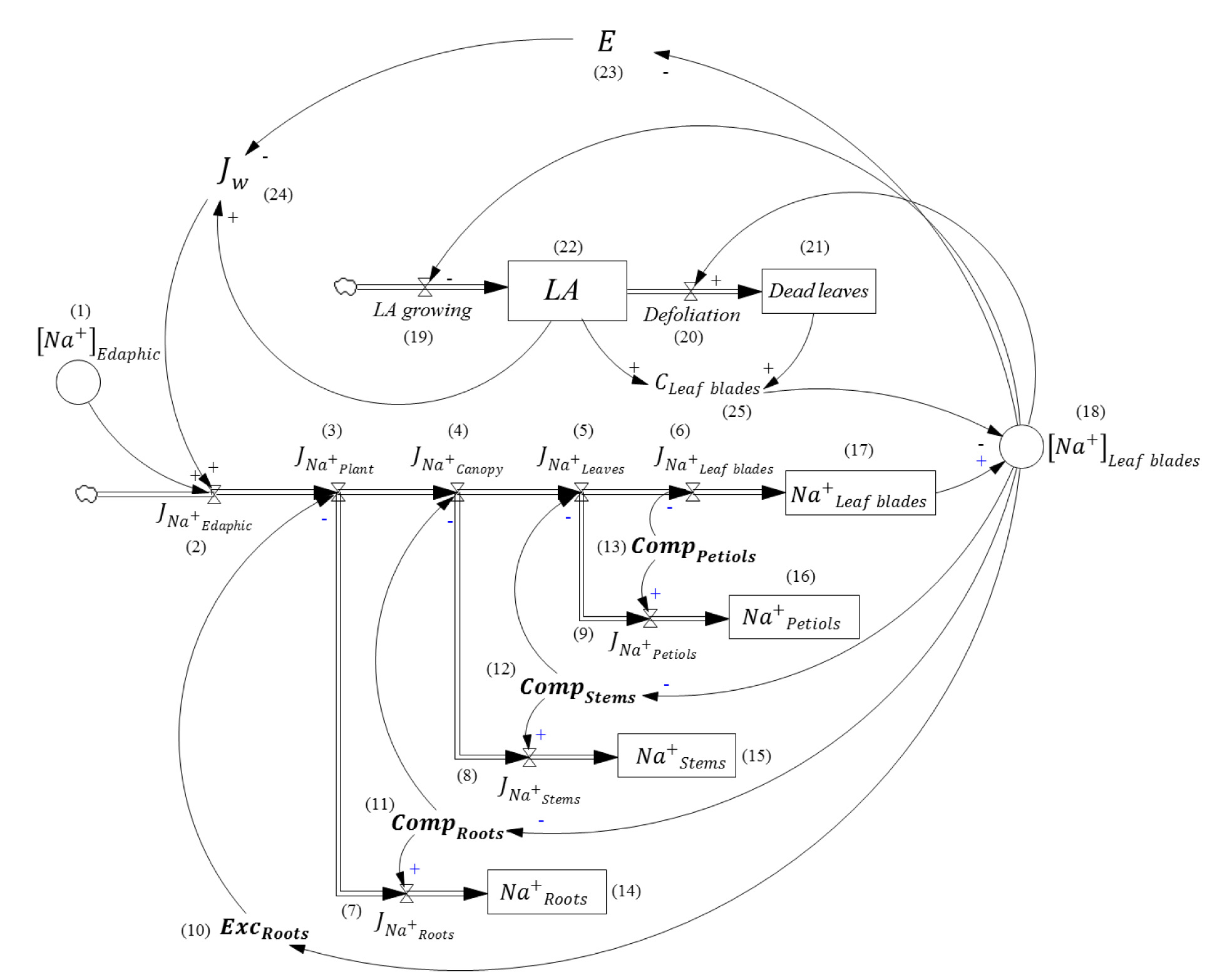
A correct selection of salt-tolerant plants should consider the relative effects of the various existing tolerance mechanisms. When toxic ions, like Na+, reach the leaves, they affect the photosynthetic apparatus, reducing plant growth and performance. Leaf concentration of toxic ions depends on exclusion efficiencies at root level, or compartmentation in organs other than leaves. On the other hand, flow within the plant depends on leaf area, transpiration rate, and soil ion concentrations. From this perspective, in a feedback process, leaf area may be, simultaneously, cause and consequence of salt toxicity. To unravel how this feedback process influences salinity damage in grapevines, a dynamic model of Na+ toxicity was developed. The theoretical model proposed a way to estimate plant exclusion and compartmentation efficiencies. Parametrization was based on a 60-days trial with potted cv. Malbec vines (Vitis vinifera L.), own-rooted and grafted onto 101-14Mgt, 1103P and Cereza, under three soil NaCl levels (0, 50 and 100 mM). The model simulated different grapevine rootstock responses to different salinity levels. These simulations evidenced the key role of Na+ exclusion in long-term tolerance. Stomatal adjustment, compartmentation and rootstock conferred vigor showed relatively minor effects.
Highlights:
- When toxic ions, like Na+, reach the leaves, they affect plant growth and performance.
- Leaf concentration of toxic ions depends on exclusion efficiencies at root level, or compartmentalization in organs other than leaves.
- A theoretical and dynamic model of Na+ toxicity proposed a way to estimate plant exclusion and compartmentation efficiencies.
- These simulations evidenced the key role of Na+ exclusion in long-term tolerance, while stomatal adjustment, compartmentation and rootstock conferred vigor, showed relatively minor effects.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.











.jpg)




