Genetic diversity among alfalfa genotypes (Medicago sativa L.) of non-dormant cultivars using SSR markers and agronomic traits
Keywords:
autotetraploid, microsatellite markers, cluster analysis, principal components analysis, generalized procrustes analysis, plant breedingAbstract
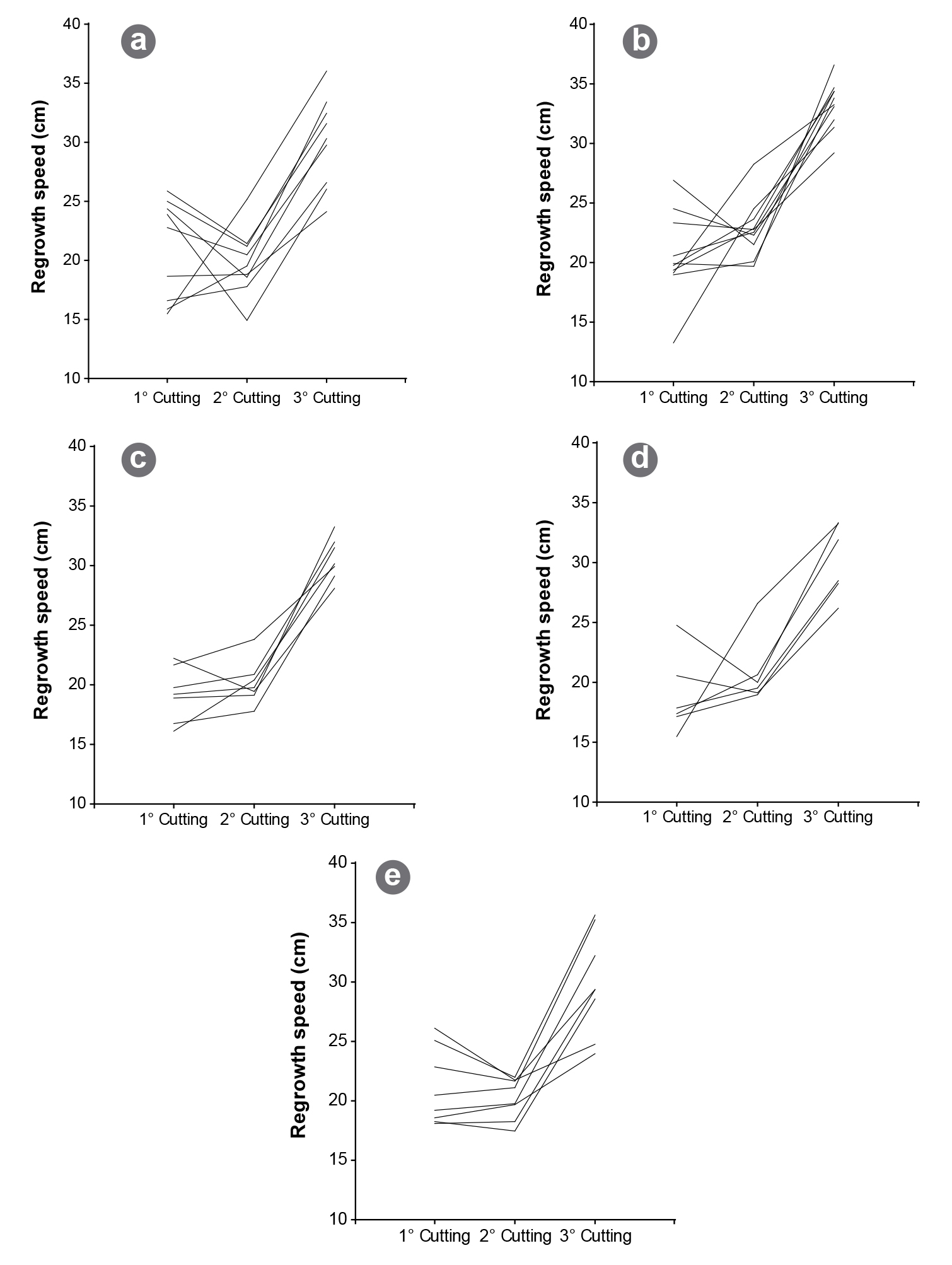
The aim of this study was to assess genetic diversity among 40 alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) genotypes of different non-dormant (FD=8) cultivars. Biomass yield, regrowth speed and reaction to spring black stem, lepto leaf spot, and rust were evaluated. Analyses of variances were performed using a mixed model to examine the agronomic variation among individuals. A principal component analysis on standardized agronomic data was performed. Agronomic data were also used to calculate Gower's distance and UPGMA algorithm. For the molecular analysis, six SSR markers were evaluated and 84 alleles were identified. The genetic distance was estimated using standard Nei's distance. Average standard genetic diversity was 0.843, indicating a high degree of variability among genotypes. Finally, a generalized procrustes analysis was performed to calculate the correlation between molecular and agronomic distance, indicating a 65.4% of consensus. This value is likely related to the low number of individuals included in the study, which might have underestimated the real phenotypic variability among genotypes. Despite the low number of individuals and SSR markers analyzed, this study provides a baseline for future diversity studies to identify genetically distant alfalfa individuals or cultivars.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.










.jpg)




